Battles
The Evolution of Reproductive Rights From Comstock to Contemporary Battles
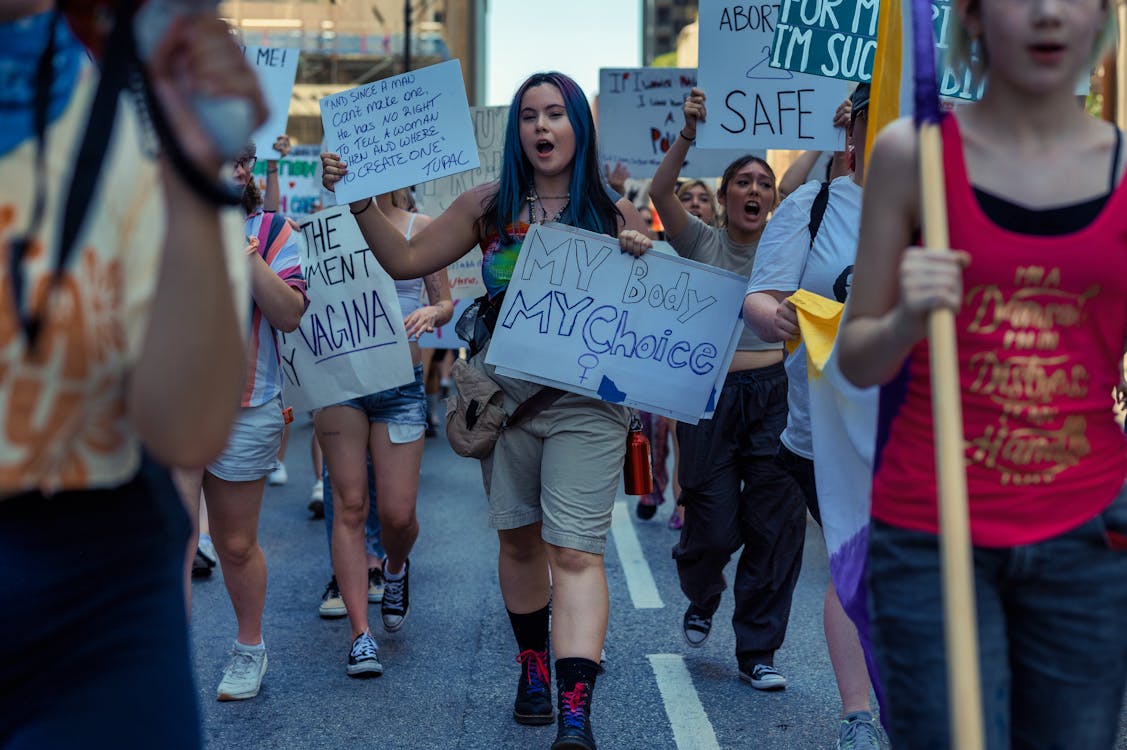
Women’s reproductive rights have long been a battleground in legal and societal debates, influencing policies, shaping court decisions, and redefining women’s autonomy. These rights encompass access to contraception, abortion, maternity care, and overall reproductive health services.
Over time, legal battles over reproductive rights have altered the course of history, reflecting changing attitudes toward gender equality and bodily autonomy.
From ancient societies to modern legal battles, reproductive rights have played a crucial role in shaping women’s status in society. The legal history surrounding these rights highlights a dynamic struggle between progress and restriction, deeply influenced by cultural, religious, and political beliefs.
In this article, we will trace the evolution of reproductive rights legislation.
Early Struggles for Reproductive Rights
The control of women’s reproductive choices emerged from deeply rooted social structures and religious beliefs across civilizations. While ancient cultures possessed knowledge of fertility control, these practices often existed in shadows, facing condemnation from ruling authorities.
Throughout history, different communities have displayed differing degrees of tolerance regarding reproductive choices. Some have accepted conventional cures, while others have enforced harsh penalties.
The 1800s marked a turning point as formal restrictions on reproductive rights took hold across Western nations.
The United States, in particular, saw the emergence of the notorious Comstock Act of 1873. This sweeping legislation criminalized the sharing of contraceptive information and materials through postal services. This law exemplified the era’s attempt to regulate women’s bodily autonomy under the guise of protecting public morality.
Anthony Comstock, the law’s namesake, gained notoriety for his zealous enforcement. He proudly documented his arrests and seizures, showing little remorse for the devastating impact on people’s lives. Legal scholar Mary Ziegler told ABC News that this included those who died by suicide due to his persecution.
The Struggle for Abortion Rights
In 1973, the landmark Roe v. Wade decision provided federal protection for abortion rights, citing constitutional privacy guarantees. For nearly five decades, this ruling served as the foundation of reproductive rights in the United States. However, it also remained a focal point of intense political and social debate.
The Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling, which reversed Roe and fundamentally altered the country’s abortion situation, changed everything in June 2022. Statista notes that this ruling left abortion rights to the discretion of individual states, resulting in significant disparities across the country.
Within a year, abortion services ceased entirely in thirteen states, while others preserved or expanded access. The result was a fragmented system of reproductive rights with profound regional differences.
In the wake of Dobbs, abortion access has depended heavily on geography. States that continue to allow abortions, particularly those adjacent to restrictive states, have become critical access points.
For example, Kansas experienced a staggering 72.2% increase in procedures after neighboring states like Oklahoma, Missouri, and Arkansas enacted bans. Similarly, North Carolina saw a 44.6% rise in abortions as restrictions tightened in surrounding areas.
These shifts highlight how access to reproductive healthcare is now largely dictated by where someone lives. This creates significant logistical and emotional challenges for patients and providers alike in this new legal reality.
The Role of Feminism and Activism in Legal Changes
Feminist movements have served as the backbone of reproductive rights progress, transforming individual struggles into collective action for systemic change. Through sustained activism, these movements have successfully challenged restrictive policies. They have also expanded the conversation beyond simple access to include comprehensive reproductive healthcare and bodily autonomy.
The impact of feminist advocacy extends beyond legal reforms to encompass healthcare safety and corporate accountability. A striking example is the recent scrutiny of contraceptive device safety, highlighted by the extensive litigation surrounding the Paragard IUD.
As per TorHoerman Law, the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System has received over 7,000 complaints, many of which have been classified as serious. This has drawn attention to the urgent need for stricter oversight of contraceptive products.
Many individuals affected by these complications have sought legal representation from a Paragard lawyer. The plaintiffs hold manufacturers accountable and advocate for patient rights. This case exemplifies how activist attention has evolved to address both access and safety in reproductive healthcare.
These movements have consistently emphasized the intersectional nature of reproductive justice, recognizing that marginalized communities face compounded barriers to healthcare access.
The Future of Women’s Reproductive Rights
Medication abortion is becoming a more and more important alternative as the field of reproductive healthcare continues to change.
Data from the Guttmacher Institute’s Monthly Abortion Provision Study reveals a notable shift in abortion methods. Medication abortions rose from 53% of all procedures in 2020 to 63% in 2023. This represents approximately 642,700 cases within the formal healthcare system.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of reproductive rights faces multiple influencing factors.
Political dynamics at both state and federal levels will continue to shape access and restrictions. Judicial interpretations of existing laws and new challenges may further reshape the legal framework.
Meanwhile, advancing medical technologies offer promising developments in reproductive healthcare, though these innovations often bring their own set of ethical and regulatory considerations.
The path forward requires sustained engagement on multiple fronts. Advocacy efforts must adapt to address both traditional challenges and emerging issues in reproductive healthcare.
FAQs
-
Why is it important to protect women’s reproductive rights?
A: Reproductive rights are fundamental human rights. Policies restricting these rights contribute to inequality and limit women’s autonomy. Supporting reproductive rights helps create a fairer, more sustainable, and inclusive world where women can make informed choices about their health, bodies, and future.
-
What is the ultimate goal of feminism?
A: Feminism aims to eliminate sexism, gender-based oppression, and inequality. The ultimate goal is to ensure full gender equality in both legal rights and everyday life. This means empowering individuals to have equal opportunities, choices, and freedoms regardless of gender or identity.
-
How many states have abortion bans?
A: As of January 2025, 17 states have enacted near-total abortion bans, with some allowing limited exceptions for rape, incest, or the mother’s health. These restrictions disproportionately impact marginalized communities. It makes access to essential reproductive healthcare increasingly difficult and inequitable.
As the future unfolds, the trajectory of these rights will depend on collective action and intersectional advocacy. It will also require a commitment to bridging the gaps in access and equity. The story of reproductive rights is far from over. It is a dynamic and ongoing narrative that challenges societies to prioritize humanity, dignity, and freedom above all else.

-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoEnchantment & Excitement: Crafting Unforgettable Event Experiences
-

 GENERAL1 year ago
GENERAL1 year agoFrom Fan Art to Original Works: The Diversity of doujindesu Creations
-

 GENERAL12 months ago
GENERAL12 months agoEngland Business Visa Requirements for American and International Citizens in 2025: A Guide for Entrepreneurs
-

 GENERAL10 months ago
GENERAL10 months agoCrossword Conundrum: The Significance of vault opener nyt crossword
-

 GENERAL1 year ago
GENERAL1 year agoLatest Trends in Men’s and Women’s Jackets for the Upcoming Season
-

 GENERAL10 months ago
GENERAL10 months agoExploring the World of nhentai.nef: A Comprehensive Guide for New Users
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoDiscovering gel ooru: The Ultimate Guide to This Unique Traditional Craft
-

 Fashion11 months ago
Fashion11 months agoBest Shampoos and Treatments from OZ Hair and Beauty for Thinning Hair: Strengthen and Revitalize Your Strands