TECHNOLOGY
Selenium WebDriver Explained for Beginners

Selenium WebDriver is a widely used framework in the software sector. But if you’re new to it, you must be wondering What is Selenium WebDriver? and How does it work? Simply put, it’s a robust automation framework that assists developers and testers in verifying whether sites are functioning according to the expectations of the users.
Web testing becomes easier and faster for all of us with Selenium and its WebDriver. It all begins with Selenium WebDriver. It is easy to use and well-supported by many programming languages such as Java and Python. Testing websites across several browsers, like Chrome and Firefox, can be accomplished with Selenium.
Selenium WebDriver: Time To Magnify The Deets
Selenium WebDriver is an automated web browser tool. It feasibly and efficiently works with all the most commonly used browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Safari. Tester can even test using Java, Python, C#, or JavaScript.
WebDriver is quick and natively supports control over browsers, so tests run smoothly and quickly. Selenium WebDriver is unique from the rest of the Selenium tools. Selenium IDE is an easy tool to record and replay tests written in simple terms.
Selenium Grid allows tests to run on several devices simultaneously. WebDriver is the primary framework used for making flexible and efficient test scripts.
You can test web applications on majorly browsers and Operating Systems (OSs) using Selenium WebDriver. It makes bug detection easier before users notice them. WebDriver is used by various organizations for web testing. WebDriver is one of the most suitable tools to learn web automation using.
Steps to Set Up Selenium WebDriver
The following are steps to set up Selenium WebDriver;
Step 1: Obtain Prerequisites
Download a programming environment such as Java or Python. A tester should install and download a suitable Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse or VS Code. Also do ensure that there is a web browser such as Chrome or Firefox already installed on your device.
Step 2: Download Selenium WebDriver Libraries
Download the Selenium WebDriver library for your chosen language from the official website. Include this library in your project in your IDE.
Step 3: Download the Browser Driver
Download the appropriate driver for your browser, like ChromeDriver for Chrome or GeckoDriver for Firefox. Put the driver file within a folder on your system. Set up the driver path in your code or system properties.
Step 4: Generate Your First Selenium Script
Open a rapid script in your IDE. Use commands such as driver.get(“https://www.example.com”) to load a web page. Incorporate actions such as button clicks or submission of a form.
Step 5: Execute the Script and Confirm Outcomes
Execute your script in the IDE. The browser will launch and execute your actions. If there are any errors, you should double-check your driver path and library configuration.
Selenium WebDriver Architecture
Selenium WebDriver employs a simple but robust architecture that can easily automate browser interactions. It bridges your test scripts to actual web browsers via special browser drivers such as ChromeDriver or GeckoDriver. The core components include the WebDriver Application Programming Interface (API), browser drivers, and browsers themselves.
When you execute a Selenium script, your program instructs the WebDriver API. The WebDriver API instructs the browser driver with commands using a protocol like JSON Wire Protocol or the W3C protocol in later versions.
The browser driver serves as an intermediary and receives commands, sending them to the actual browser. The browser acts, such as a button click or page open, and returns the results to your script through the driver.
This bidirectional command flow is compatible with all the major browsers. There is a distinct driver for every browser, and therefore, you can switch from Chrome to Firefox, Edge, or Safari by modifying the driver.
Clean segmentation of browsers, drivers, and scripts makes Selenium WebDriver easy to implement and suitable for cross-browser testing. This design allows the browsers to be controlled by the testers for web automation in a consistent manner.
Basic Selenium WebDriver Commands
Selenium WebDriver employs straightforward commands to communicate with browsers and automate web activities. You begin by opening a browser window using a command such as driver = webdriver.Chrome().
This instructs Selenium to employ Chrome, although you can choose other browsers as well. To open a website, use the driver.get(“https://www.example.com”). This code opens the page in your browser.
To move from one web page to another, you must locate elements such as buttons or text fields. Selenium gives you options of how to locate elements by ID, name, class, XPath, or CSS selector.
To locate a field by its ID, say, use driver.find_element(By.ID, “username”). If there is no ID, you can use XPath or a CSS selector to locate what you want.
You can act upon finding elements. Click on a button using.click(), send text using.send_keys(), and submit a form using.submit(). You can select options from drop-down menus, check boxes, or retrieve text from the page.
In short, you close the browser with driver.quit() or driver.close(). That is how you finish your session and release memory. These simple commands allow you to log in, search, enter forms, and verify if websites function correctly. Mastering these steps is the secret to creating your web tests with Selenium WebDriver.
Working with Different Browsers
Selenium WebDriver supports all major browsers, allowing automated tests to be run without altering test code. Each browser requires a specific driver, which can be downloaded and configured in the system settings or a program. For Safari, the driver is packaged with the browser on macOS, so no extra setup is required.
Running your test cases with different browsers assists in the determination of browser-dependent bugs and guarantees that your site functions across all browsers. Interchanging browsers quickly in Selenium only requires changing the driver employed in your environment. Cross-browser testing is useful for trustworthy web testing and ensuring a similar experience everywhere.
Handling Web Elements and User Interactions
Selenium WebDriver automates web and interacts with web elements like buttons, text boxes, drop-downs, radio buttons, and checkboxes using methods like ID, name, class, XPath, or CSS selector to enable users to perform complex actions using mouse and keyboard.
Selenium WebDriver also provides wait strategies for web pages to load, making tests stable and less prone to fail if the page is slow. These traits enable Selenium WebDriver to test most user interactions and ensure a flawless website for everyone.
Writing and Running Your First Test Script
Writing your first test script using Selenium WebDriver is easy and an excellent way of getting started with automated web testing. Use the following steps to develop and execute your first script.
Step 1: Set Up Your Project
Ensure Selenium WebDriver is properly installed and your browser driver is set up. Open your IDE and initialize a new project for your test script.
Step 2: Start the Browser Session
Set up the browser you wish to use, say Chrome or Firefox. This opens a new browser window for testing.
Step 3: Go to the Website
Inform Selenium where to go on the web by providing the URL. The browser loads the page you wish to test.
Step 4: Find Web Elements
Specify actions you need to take on certain elements, for example, text fields or buttons. Utilize simple ways to locate such elements by ID, name, or other properties.
Step 5: Perform Actions
Fill in fields with text, click buttons, or submit forms. These activities mimic what a genuine user performs on the site.
Step 6: Check the Results
After these steps, verify whether the expected results are visible. Observe messages or page changes to ensure that your test was successful. Utilize assertions to verify actual and expected results.
Step 7: Close the Browser
Finish the test by closing the browser session. This releases resources and completes your test.
Step 8: Review and Improve
In case of errors, inspect your script and configuration. Provide comments for understanding. Practice and modify your scripts as you come to know more.
Best Practices to Work With Selenium WebDriver for Beginners
You can easily start with Selenium WebDriver if you adopt some quality best practices. Following these best practices will enable you to write efficient and stable test scripts:
- Structure Your Scripts
Organize your test scripts in properly named directories and bestow them with descriptive names. This is because it is easy to locate, modify, and restructure as the project is expanding.
- Write Clean and Simple Tests
Begin with simple and concise scripts. This is easier for learning what a script does and debugging.
- Use Assertions
Add assertions to determine if your test results are real. Assertions inform you whether a test passed or not, making your tests stronger and valuable.
- Debug and Keep in Order Periodically
Review error messages and print statements to locate issues. Debug issues step by step. Refresh scripts every time the website is refreshed to maintain your tests running and operating.
- Keep Learning
Practice writing and running scripts regularly. Learn from errors and continue practicing your skill. Creating good habits here will come in handy in tackling larger projects.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting of Selenium WebDriver
New users of Selenium WebDriver will have some common problems during their initial exposure. Learning how to identify and debug them will enable you to test easily. The following are common challenges;
- Driver and Path Issues
Most beginners do the driver wrong or never set the path. Make sure you have the correct driver for your browser and that the path is properly set. Check through your code for spelling errors.
- Element Not Found
Sometimes, Selenium is unable to find elements because pages are too slow to load. Use waits so the elements get an opportunity to display. This steadies your tests.
- Compatibility Issues
Driver or browser bugs can cause failures. Make sure your browser and drivers are updated to prevent these issues.
- General Troubleshooting Tips
If you see your test failing, inspect the error message carefully. Look up on the internet for a solution or go through an example. If you are stuck, get assistance from forums. Troubleshooting is a skill worth having, and with practice, you will find yourself more proficient at fixing issues.
Cloud Testing for Making Selenium WebDriver Easier
Cloud testing is critical for simplifying the use of Selenium WebDriver, especially when dealing with cross-browser testing at scale. Setting up and maintaining local environments can be time-consuming, error-prone, and limiting when it comes to real-world device coverage.
One such platform that makes this easier is LambdaTest. It is an AI-native test execution platform that allows you to run both manual and automated tests across 3000+ real browsers and OS combinations, eliminating the need for complex local setups.
If you’ve ever asked, “What is Selenium, and how can I use it effectively at scale?”, LambdaTest provides the answer. When used with Selenium WebDriver, it enhances your automation efforts by enabling parallel execution, which significantly accelerates release cycles and improves test coverage.
With real-time analytics, seamless CI/CD integrations, and powerful debugging tools, LambdaTest helps your QA team identify issues faster and work more efficiently.
By moving your Selenium testing to LambdaTest, you gain the ability to scale reliably, reduce infrastructure costs, and ensure your web applications run smoothly across any browser or device.
Conclusion
To sum up, Selenium WebDriver is an excellent automation tool for web testing. It directs new beginners to learn how to test websites in other browsers. Using basic commands, you can open pages, click buttons, and verify results.
Begin with simple scripts and do it regularly. You should follow the best practices to make your tests fit and healthy. Debug and continue if you get stuck. Selenium WebDriver is relied upon by thousands of testers and organizations. Embark on this journey today and discover how easy web automation can be.
TECHNOLOGY
Ensuring Workplace Safety: The Critical Role of Proof Load Testing
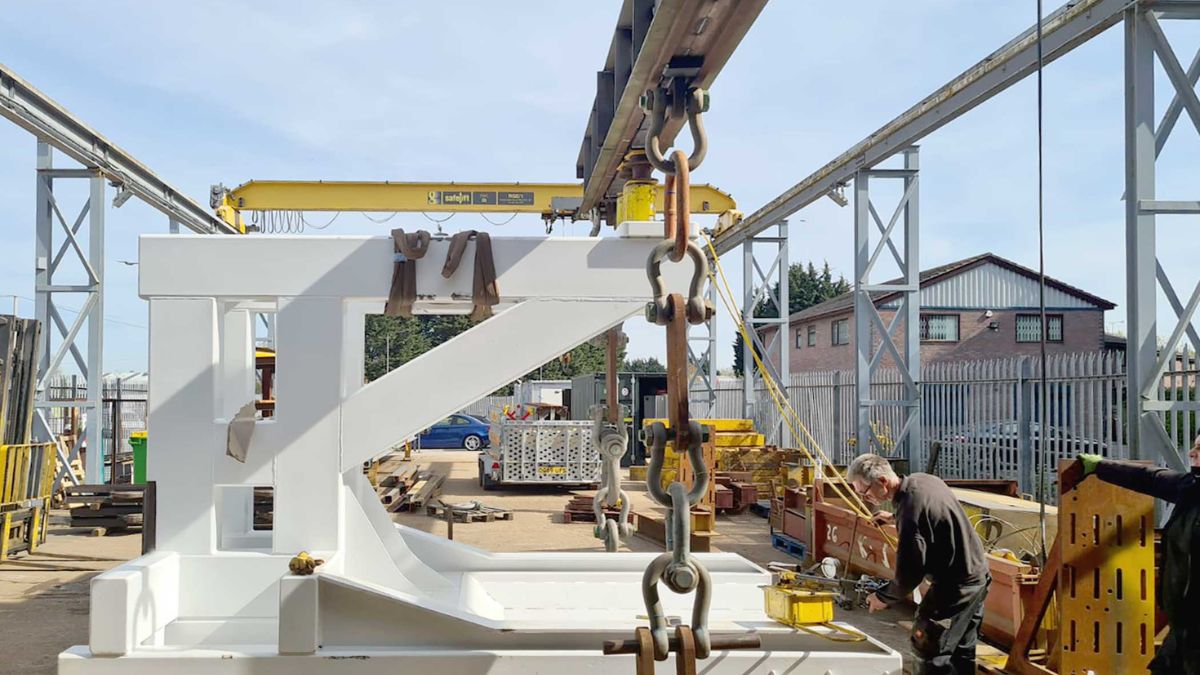

Understanding Proof Load Testing
Maintaining a safe working environment is not just about creating policies; it is also about following through with essential safety procedures. In industries such as construction, shipping, and manufacturing, lifting equipment is the backbone of operations. The failure of a lifting device can cause catastrophic injuries and significant financial losses. That is why proof load testing is regarded as a foundational aspect of safety management.
Proof load testing involves applying a controlled load, often exceeding the equipment’s rated capacity, to verify its ability to perform safely under stress. This proactive initiative is designed to catch structural weaknesses or fatigue before equipment is put to regular use. For those interested in regional solutions, proof testing Houston, TX, can help ensure your lifting devices meet the required standards.
During proof load testing, certified professionals use specialized tools to simulate real-world loading conditions. This thorough approach is not just about equipment validation; it also serves as a critical safeguard for workers and reduces the likelihood of operational downtime due to unexpected equipment malfunctions.
According to guidelines established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), this kind of safety testing is both a best practice and a regulatory requirement for many types of lifting machinery.

Equipment Requiring Proof Load Testing
Various types of lifting equipment, both large and small, require regular proof load testing. Among the most critical are:
- Overhead and gantry cranes
- Hoists and winches
- All forms of lifting slings, including wire rope, chain, and synthetic options
- Shackles, hooks, lifting beams, and other critical rigging hardware
The failure of any of these components during use can result in dropped loads, injuries, or fatalities. This necessity makes routine inspection and proof-load verification a non-negotiable part of maintenance schedules.
Frequency and Triggers for Testing
When should proof load testing be conducted? Safety experts and industry regulations point to several key triggers:
- Before the initial use of new equipment
- After any significant modifications or repairs
- As part of scheduled, periodic reviews, frequency often depends on usage cycles and environmental conditions
OSHA guidelines mandate that custom lifting devices be tested to 125 percent of their rated load before being put into service. These proactive steps are essential for both brand-new equipment and older devices that have seen repairs or heavy use.
Consequences of Neglecting Proof Load Testing
Failing to perform scheduled or required proof load tests can have serious repercussions. The obvious impact is the increased risk of workplace accidents and injuries when equipment fails unexpectedly. Companies can also be left vulnerable to:
- Costly legal actions and OSHA fines for non-compliance
- Significant damage to reputation that affects both employee morale and client relationships
- Permanently tarnished business credibility due to well-publicized safety failures
Work-related fatalities or severe injuries due to preventable equipment failures are catastrophic for everyone involved. The direct and indirect costs of insurance increases and litigation, as well as workforce disruption, can cripple organizations that do not make safety testing a regular priority.
Best Practices for Conducting Proof Load Tests
To maximize the value and reliability of proof load testing, experts recommend several best practices. These include enlisting certified testing professionals familiar with current OSHA and ASME requirements, using well-maintained, calibrated equipment, and maintaining detailed documentation of all results. Regularly reviewing and updating testing protocols ensures your organization keeps pace with technological advances and regulatory changes.
Training personnel on current test methods and maintaining detailed records are just as vital as the tests themselves. These records can be essential for audits, legal matters, and ongoing risk assessments. For continued industry insight and news, reputable sources such as Safety+Health Magazine provide extensive coverage on industrial safety developments.
Final Thoughts
Proof load testing is a non-negotiable pillar of workplace safety for organizations utilizing cranes, slings, hoists, and related equipment. It provides unequivocal evidence of an equipment’s safety and fitness for use, helping to prevent workplace injuries, avoid non-compliance fines, and foster a robust safety culture. The small investment of time and resources in regular proof load testing is far outweighed by the benefit of accident prevention, compliance, and operational peace of mind.
TECHNOLOGY
Essential Elements Every Contact Form Should Have
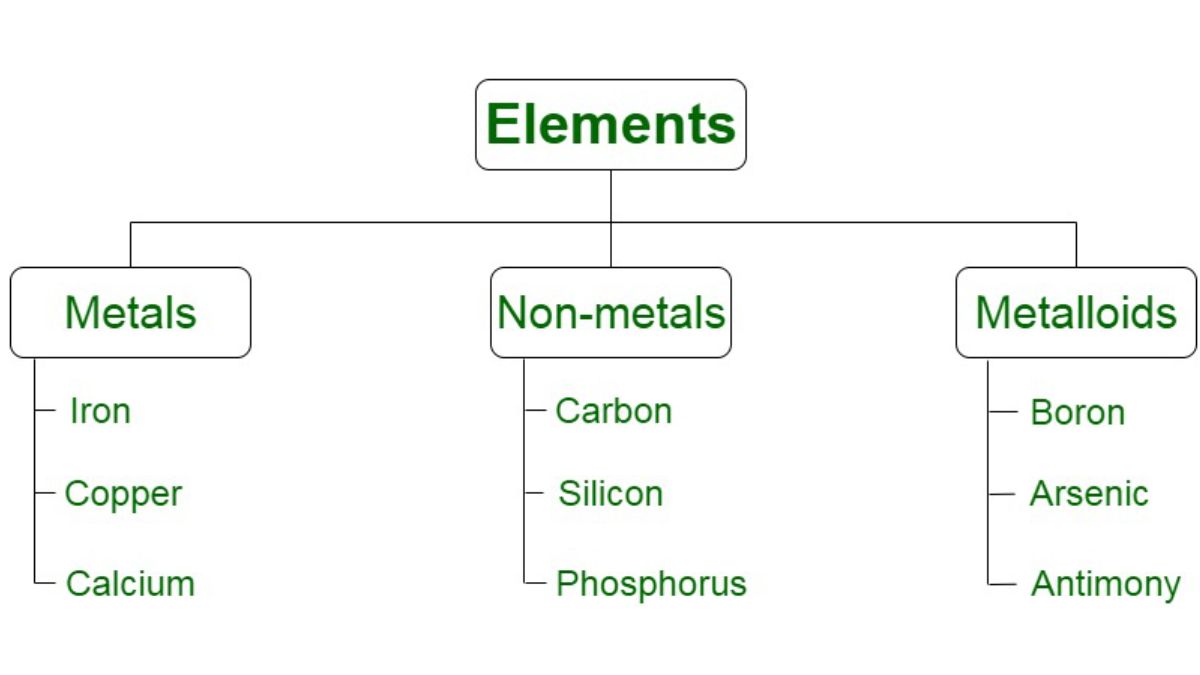
Contact forms play a pivotal role in how businesses receive inquiries, answer questions, and engage with their customers. Whether you are running a small business website or a corporate portal, making your contact form inviting and functional helps ensure visitors feel comfortable reaching out. Effective forms streamline communication, improve user satisfaction, and support business growth. For anyone looking to optimize their website’s contact touchpoints including those interested in car maintenance Bellevue, WA incorporating the right elements is key.
While strong design and ease of use are critical, there is much more to consider. Accessibility, clarity, robust security measures, and search optimization all contribute to the success of a contact form. By carefully balancing these elements, businesses can ensure their contact forms drive meaningful engagement and provide a better user experience for everyone involved.
Welcome users, encourage interaction, and make contacting your business as seamless as possible. In this guide, you will find actionable strategies and best practices for building the perfect contact form, whether for an auto shop in Bellevue or any other industry seeking to improve customer communication and conversion rates. According to the Nielsen Norman Group, even the smallest tweaks to form design can make a noticeable impact on your business’s ability to generate leads and answer customer inquiries.
Keep It Simple: Limit Fields to Essentials
Users are far more likely to fill out a contact form that asks only for essential information. Overly complicated forms with too many required fields tend to discourage visitors. Instead, focus on gathering the necessary data to act on customer requests. Typically, this means asking for:
- Name
- Email Address
- Subject or Inquiry Type
- Message
User fatigue can occur when forms feel laborious to use. By sticking to the basics, you show respect for a visitor’s time and increase the likelihood of receiving completed forms. This simple approach aligns with findings from major UX studies published by the Nielsen Norman Group, which show that shorter forms outperform longer ones in terms of submission rates and user satisfaction.
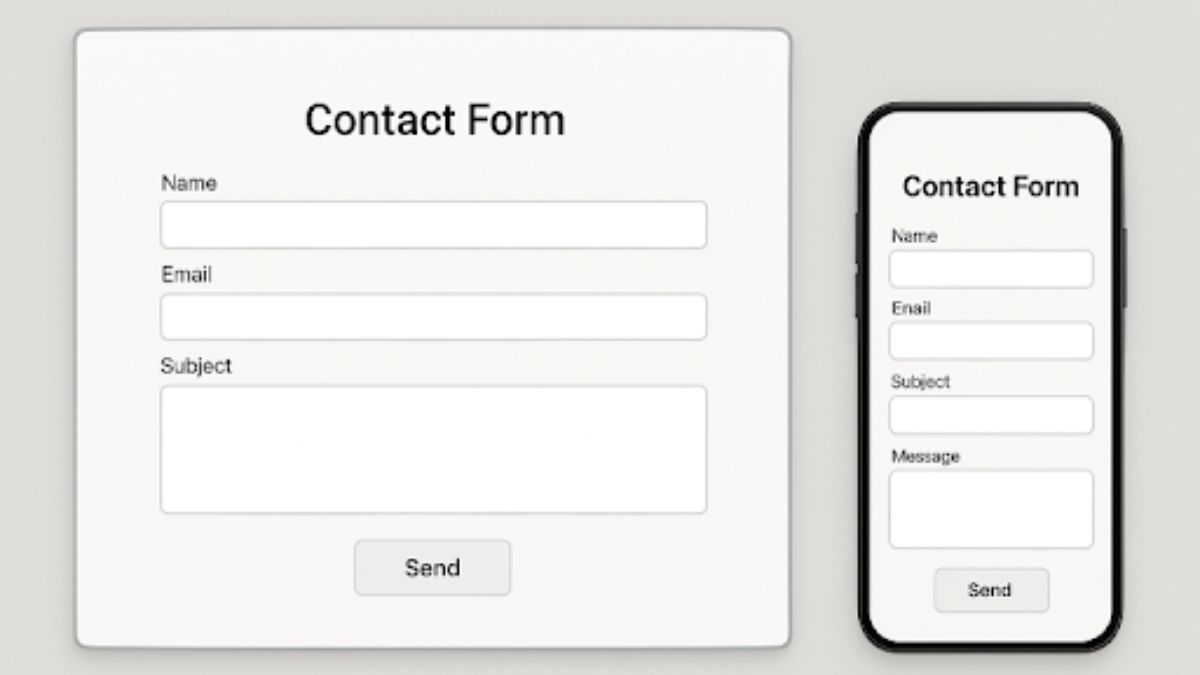
Ensure Accessibility and Mobile Responsiveness
It is crucial that every contact form is accessible across devices and to users of all abilities. With mobile traffic now accounting for the largest share of internet use, ensuring mobile responsiveness should be a top priority. This includes designing forms that automatically resize for smaller screens and remain easy to use on smartphones and tablets.
- Design with flexible layouts for different screen sizes
- Label all fields clearly for assistive technologies like screen readers
- Use placeholder text and error prompts that provide meaningful instructions
Accessibility is not just a best practice for compliance, but also expands your reach to all potential customers, including those with disabilities or who rely on technology to interact with your site.
Use Clear and Conversational Field Labels
Confusing or technical language can frustrate users. Field labels should be simple, familiar, and conversational. Instead of using internal terms such as “User Identifier” or ambiguous labels like “Details,” stick to what users expect. “Full Name,” “Your Email,” or “How can we help?” are examples that feel inviting and clear. This friendly approach reduces errors and increases the likelihood that users complete and submit your form.
Implement Strong Calls-to-Action (CTAs)
The submit button is an opportunity to boost conversion rates. Rather than settling for generic directives, make your calls to action clear and appealing. Personalized, enthusiastic CTAs like “Get in Touch with Us Today,” “Let’s Start a Conversation,” or “Request a Free Consultation” create urgency and excitement, encouraging users to reach out and connect.
Provide Feedback on Submission
Once a visitor sends their inquiry, displaying an automated confirmation message or sending a follow-up email is crucial. This feedback builds trust and reassures users that their submission was successful. It also sets expectations on how soon they might receive a response, reducing uncertainty and improving the overall user experience.
Display Alternative Contact Information
While many users enjoy the convenience of online forms, not everyone will feel comfortable using them. To ensure you are accessible to all preferences, include supplementary contact options prominently on your page. These can include your phone number, email address, live chat, or even social media links. Providing a range of alternatives improves trust and shows your commitment to open lines of communication.
Reduce Spam with CAPTCHA or Honeypots
Preventing spam is essential for maintaining a clean inbox and protecting your business from bots. Implementing a CAPTCHA, reCAPTCHA, or honeypot field is an effective way to block automated junk while keeping the form experience as easy as possible for real users. However, choose captcha solutions that balance effectiveness with usability to avoid frustrating legitimate visitors.
Optimize for SEO with Relevant Keywords
Contact forms can also improve your website’s search visibility when strategically optimized. Use clear, keyword-rich headers and meta descriptions, and ensure your form and surrounding content employ natural language that reflects your business and what you offer. Alt-text for icons or images, along with a logical, structured layout, further help search engines understand your page, potentially driving more organic traffic to your site.
Final Thoughts
With these essential elements in place, businesses can create forms that are not only attractive and functional but also capable of supporting high levels of user interaction, satisfaction, and conversion. These optimizations will help your contact page deliver real results and foster long-term relationships with your audience.
TECHNOLOGY
Safe and Practical Approaches to Old Oil Tank Removal
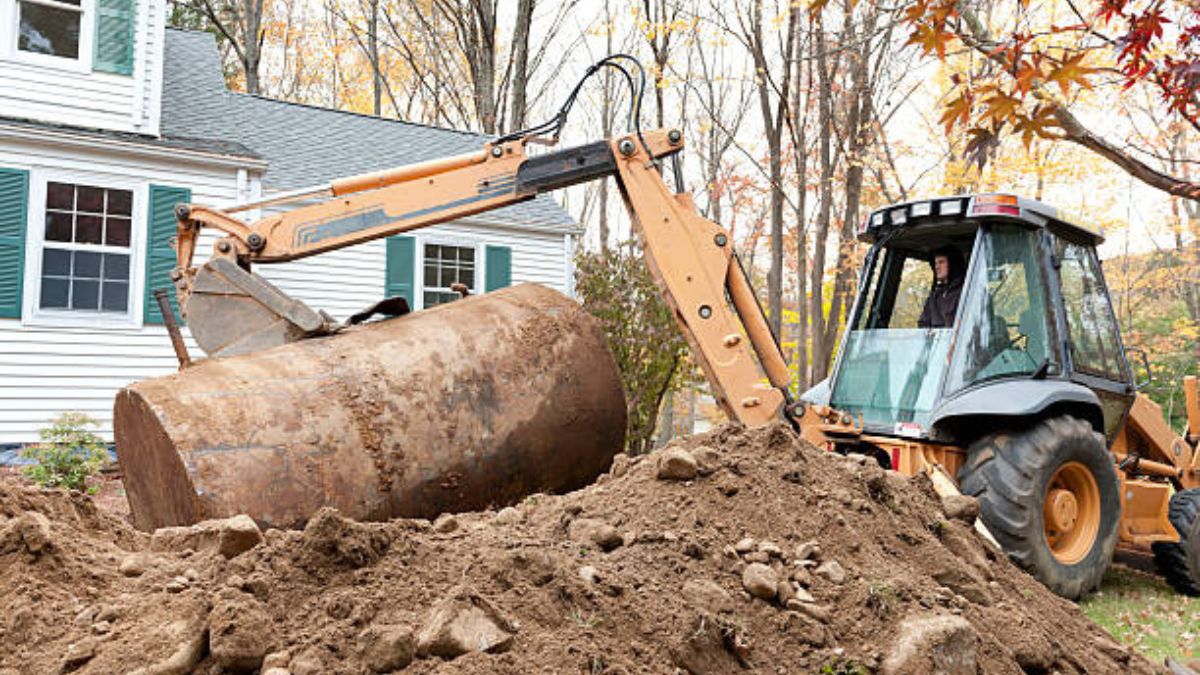

Old oil tanks, especially those installed decades ago, can pose significant safety and environmental risks to homeowners. Understanding how to safely manage the removal process prevents costly complications, legal issues, and health hazards. Homeowners should always prioritize best practices for safety, legal compliance, and environmental stewardship when considering oil tank removal. If you are searching for assistance, oil tank services Greenwood Lake, NY are available to provide guidance and hands-on help for these sensitive projects.
Identifying and removing out-of-date oil tanks is not only a matter of property maintenance but also an essential step in protecting groundwater, soil, and nearby inhabitants. Decommissioned or abandoned tanks can become liabilities for homeowners, especially if leaks go unnoticed. Professional removal ensures the proper handling of potential hazards and prevents structural damage, pest infestations, and future resale problems.
Homeowners should never attempt to remove tanks on their own. Trained professionals have the expertise, tools, and certification required to ensure the process is safe and compliant with state and federal regulations. Securing proper permits, hiring experienced contractors, and documenting every step help safeguard you from future remediation expenses or legal fines. When handled correctly, oil tank removal is a straightforward process that protects your home, your neighborhood, and the environment.
Understanding the Risks of Old Oil Tanks
Many residential oil tanks, particularly those placed before the 1980s, are vulnerable to rust, cracks, and leaks that allow oil to escape into the surrounding environment. Oil spills from neglected tanks can contaminate soil and groundwater, posing health risks and affecting drinking water quality. The costs of remediating an undetected leak can be staggering for homeowners. In addition to environmental threats, old tanks may attract rodents and insects or collapse, posing a risk of injury or property damage.
Identifying these risks early is the best defense against expensive restoration projects and liability claims. Homeowners are encouraged to check for signs of corrosion, leakage, or strong petroleum odors around their property. Even above-ground tanks are susceptible to these dangers after years of service and exposure to the elements.
Initial Assessment and Planning
Before beginning the removal process, a comprehensive assessment is mandatory. Licensed contractors can use advanced technologies such as ground-penetrating radar to locate underground tanks and determine their size, contents, and condition. This evaluation guides the creation of a safe removal plan, which forecasts the scope of work, required materials, costs, and potential challenges at your specific site.
A thorough inspection will also identify any pre-existing contamination or damage, which is crucial for planning effective remediation. Homeowners benefit from requesting a detailed written report from their contractor that documents the findings and outlines the proposed steps. Clear communication at this stage helps avoid misunderstandings or surprise expenses later. According to The New York Times’ homebuyer guide, assessing environmental risks is a vital aspect of property maintenance and transfer of ownership.
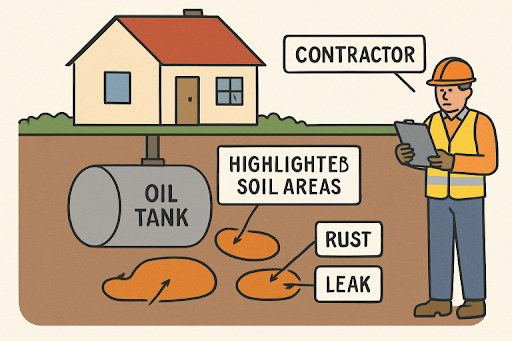
Obtaining Necessary Permits
Removing an oil tank is a regulated task in most states and municipalities. Obtaining the appropriate permits is crucial to ensure your project complies with local health, safety, and environmental codes. This typically involves submitting documentation, such as site diagrams and removal plans, to local or state agencies for review and approval. Notifications may also be required before excavation or site-disturbing activities. Complying with regulatory requirements can spare you costly fines and guarantee that the project is approved for future property sales or insurance purposes.
Engaging Professional Services
Professional assistance is a necessity when handling oil tank removal. Licensed contractors are certified to perform decommissioning, extraction, and transportation of hazardous materials in accordance with legal standards. They are equipped with proper safety gear and machinery for pumping out remaining fuel, cleaning tanks, and disposing of contents at regulated facilities. Choosing skilled contractors ensures due diligence and minimizes both health and legal risks. Always verify references, licensing, and insurance before signing a contract with a removal company.
Safe Removal Procedures
- Pumping any remaining oil from the tank and thoroughly cleaning the interior to eliminate flammable residues.
- Cutting open larger tanks, if needed, for safer extraction and easier handling.
- Excavating and lifting the tank from the ground with minimal disruption to landscaping and other utilities on the property.
- Monitoring for potential leaks or spills during every stage and preparing containment measures in advance.
Each step requires careful planning and strict adherence to safety protocols to protect the environment and ensure homeowner safety.
Soil Testing and Remediation
After an oil tank is removed, environmental specialists conduct comprehensive soil testing in the former tank area. This testing checks for trace contamination that may not be immediately visible. If pollution is found, remediation strategies might include soil excavation, chemical treatment, or bioremediation to restore the property’s safety and ecological health. Quick remediation limits ongoing legal risks and enhances property value.
Proper Disposal of Tank Materials
Old oil tanks and residual waste must be transported to approved disposal or recycling facilities in accordance with federal and state standards. Hazardous materials are processed to prevent environmental damage and ensure public safety. Contractors usually provide a manifest or a certificate of disposal that demonstrates compliance with waste management regulations. Improper disposal not only risks environmental damage but can also subject owners to severe legal penalties.
Site Restoration and Documentation
Once contaminated soil and the tank have been removed, the property should be restored to its original or improved condition. Contractors will backfill excavated areas and may recommend landscaping or erosion control as needed. Homeowners must retain all documentation, including permits, inspection reports, remediation summaries, disposal manifests, and related correspondence. These records serve as proof of compliance and are essential for future disclosures, refinancing, or sale of the property.
Final Thoughts
Adopting these safe and practical strategies for old oil tank removal shields homeowners from avoidable risk, preserves property value, and demonstrates environmental responsibility. Local professionals and national authorities provide valuable resources and expertise to support safe, legal, and efficient oil tank decommissioning.
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoEnchantment & Excitement: Crafting Unforgettable Event Experiences
-

 GENERAL1 year ago
GENERAL1 year agoFrom Fan Art to Original Works: The Diversity of doujindesu Creations
-

 GENERAL11 months ago
GENERAL11 months agoEngland Business Visa Requirements for American and International Citizens in 2025: A Guide for Entrepreneurs
-

 GENERAL10 months ago
GENERAL10 months agoCrossword Conundrum: The Significance of vault opener nyt crossword
-

 GENERAL1 year ago
GENERAL1 year agoLatest Trends in Men’s and Women’s Jackets for the Upcoming Season
-

 GENERAL10 months ago
GENERAL10 months agoExploring the World of nhentai.nef: A Comprehensive Guide for New Users
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoDiscovering gel ooru: The Ultimate Guide to This Unique Traditional Craft
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoExploring the World of NHentai: A Comprehensive Guide to nhentai.met
